Computer Vision for Augmented Reality & Virtual Reality
Tilottama Goswami
ProfessorExploring Computer Vision for Augmented and Virtual Reality: A Dive into Future Technologies
Welcome! I’m glad you’re here to explore the fascinating world of Computer Vision in terms of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality. My name is Taloa Goswami, a professor in the Department of Information Technology at the Mai College of Engineering in Hyderabad, India. My career spans over 23 impactful years in academics, industry, and research, with focus areas in computer vision, image processing, and machine learning.
Introduction to Metaverse, Virtual Reality, and Augmented Reality
Living in a world that's changing rapidly due to technological advancements can be both exciting and daunting. It's crucial that we understand how these new technologies work and their potential to revolutionize the way we interact with our environment. Such a game-changing realm is the world of Metaverse, Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR).
- Metaverse: The term "metaverse" derives from "meta", which means beyond, and "verse", which stands for universe. Essentially, the metaverse refers to a virtual universe where humans and digital avatars co-exist and communicate within a community. This digital universe is considered the superset of other digital realities including AR and VR.
- Virtual Reality: VR is a computer-generated simulation that offers an immersive experience where users can interact within a 360-degree digital environment.
- Augmented Reality: AR overlays digital elements onto the real world, thus augmenting our physical environment with additional digital information and enhancing interactive experiences.
Understanding key concepts
A core principle in understanding the metaverse, VR, and AR is the notion of 'simulation' - the concept of imitating real-world processes in a virtual environment. This can be experienced through sensory organs such as sight, touch, taste, and hearing. For instance, by using VR headsets or AR applications on our smartphones, we can enjoy an immersive digital experience that feels incredibly real.
Computer Vision's Role in AR and VR
At the heart of these advancements is the field of Computer Vision, an arm of artificial intelligence. It involves enabling computers to see, interpret, understand and make informed decisions based on visual data.
Consider this example: you're looking at a plate of fruits and you want to identify all the different types of fruit. As a human, we can observe, recognize each type of fruit, and finally list out all the fruits. Computer Vision serves to automate these tasks. A sensing device captures the image, an interpreting device recognizes each fruit, and finally, it provides a list of the fruit.
Computer Vision Tasks in AR and VR
- Object recognition and tracking: This involves not only detecting and recognizing a particular object (like a car or bus) but also tracking its movement, speed, and potential accidents.
- Image Classification and Semantic Segmentation: Here, an image is classified (e.g., it is recognized as 'a cat') and then individual objects or features in the image are segmented into meaningful clusters.
- Feature Extraction: This involves picking up key features of objects, such as edges or curvatures.
- Optical Character Recognition: This task identifies written characters or alphabets.
In order to develop software for AR and VR, all the above tasks need to be accomplished in the initial stage to provide an immersive and interactive user experience.
Case Study: Health and Fitness
An interesting application of these technologies can be found in the health and fitness industry. For instance, many companies are now creating AR and IoT-enabled treadmills that can simulate different environments, facilitating home-based training for mountaineering or trekking.
Computer Vision in Various Industries
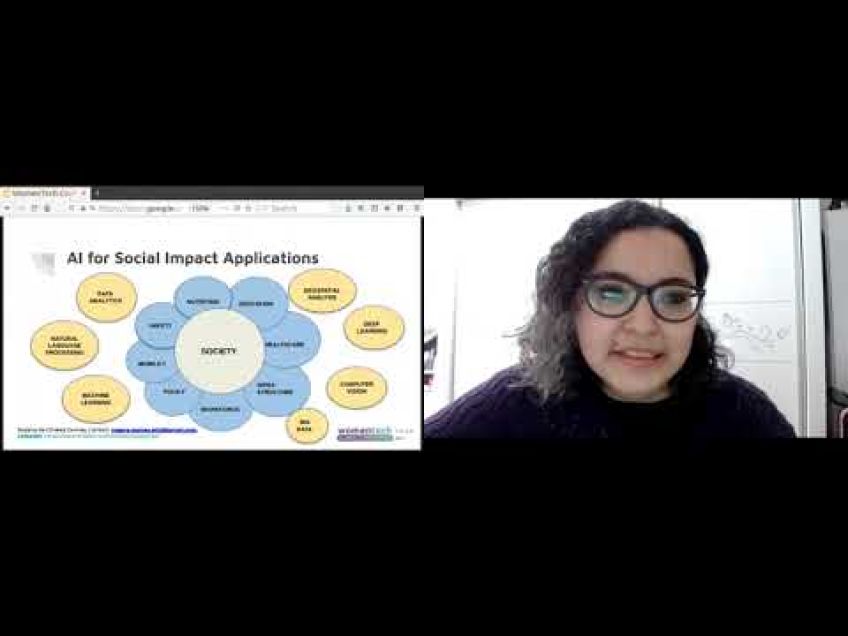
Computer Vision alongside AR and VR has wide-reaching applications in several industries, including:
- Tourism: AR applications based on GPS locations provide information overlays on real-world locations, like restaurants and coffee shops.
- Architecture: Architects and clients can use AR for overlaying 3D digital content onto 2D plans.
- Educational Learning: Virtual reality can enhance interactive learning, enabling students to interact with each other in a virtual world.
Future of AR and VR
As we move forward, it's evident that the future of technology lies significantly in the realms of VR and AR. According to Gartner's 2023 strategic technology trends, the metaverse is identified as a major future trend. In conclusion, VR and AR cannot exist without computer vision because it provides the fundamental ability to understand and interact with digital landscapes.
Remember, while this technology may still be relatively nascent, we're on the cusp of a revolution. Let’s get ready, for the possibility of where these advancements could take us, is indeed limitless. Until next time, Thank you!
Video Transcription
Namaste. Greetings. One and all. I am Taloa Goswami, working as a professor in the Department of Information Technology Mai College of Engineering from Hyderabad, India. I have overall 23 years of experience including industry, academics and research. My areas of interest are computer vision, image processing and machine learning.
I feel honored to be a part of Women Tech Global Conference 2023. Thank you for giving me this opportunity. The title of my talk is Computer Vision for Augmented Reality and virtual reality. The world of today is changing at a rapid pace. Advances in technology is helping us to explore and interact with the digital environments in ways that were unheard of a few years ago. The potential of revolutionizing how we interact with the world around us is tremendous. So let's take a brief dive into the key concepts surrounding this topic. I'll walk through the basic terminology and the concepts to get you familiar with the subject. So now let's get started. The topics which related to this title is Metaverse, Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, computer vision, computer vision algorithms, which will be used for the AR and the VR the applications of the virtual reality and augmented reality and uh very brief about the development environment.
So in this, the in this figure, we are moving from reality to the virtual reality. So there were sensory organs, the sight, taste, smell, touch, hearing, all of these can be felt in a simulated environment and that we call an immersive environment. So the reality which we are getting through these gadgets, smartphones, haptics, the VR goggles, speech recognition, interacting with the machine that gives us a feeling of a reality which is in augmenting the universe in which we are now. So that is a virtual world. What is metaverse meta means beyond and versus universe. So something beyond universe. And we mean by the virtual universe where the humans and avatars coexist as a community and the presence is felt by communicating with each of the stakeholders in this ecosystem that is the superset of the virtual reality. There are three pillars of the metaverse. The first one is feeling of the presence of oneself. Second is feeling of the special presence that is of the environment. The third one is creating an impression of presence of the others. It is not an isolated world where many of the stakeholders like AFTA humans are coexisting.
Let us see. OK. Uh Here, the types of metaverse are augmented reality, virtual worlds and extended reality. The augmented reality is basically overlaying the digital into the user's own world. The virtual world is totally immersive in the 3d environment. And the extended reality is the including the virtual reality, augmented reality and mixed reality. So the more the word is metaverse, which is the super, the super set where we are going beyond the universe, that is the virtual universe where humans of task coexist and the presence is also felt. So there are three pillars of the metaverse. The one is feeling of oneself as a jumbo or a Jami or a Ruth Thabo Swami. And then there is a feel of spatial presence that is an immersive experience. And though I I may not be reality in reality, I may not be venturing out in this valley, but I may have a virtual feeling of being in the valley. And the third one is making presence of the others by communicating with them, whether it is afar or whether it is a human.
So the virtual reality, it is a computer generated simulation and it gives you an immersive experience and the user can move around in all the 360 degrees can manipulate the objects. So there are two types of virtual reality. One is the non immersive, which is used for training simulation where we are focusing only on a part of the machine where we want to study and we want to know the uh uh understand the know how of that um equipment. The second one is the fully immersive where it is a gaming and entertainment, it is not only the goggles, but you will be, we will be having many gadgets like haptics, uh sound and some uh sensors to make us feel the maximum number of sensory organs can be felt using this fully immersive virtual reality.
Now coming to the augmented reality, it is basically your real environment and the digital content is overlaid at the top of it to get an interactive experience. So it is augmenting the real world here. The real world is having so there are augmented realities, having four types marker based marker, less projection based and super imposition based. So in this, if you see this is the marker and hence the marker is replaced by digital information here on this particular location of the garden.
The dinosaur is getting overlaid here. The bone structure of the arm is overlaid after the arm has been identified or detected. So just projecting into it, the super imposition one creates an illusion of mixed reality. So you're having one template like a Snapchat and then you have a mixed reality, but the virtual object is placed on the top of the real scenes. So uh the question was AAA any guess on what type of the A R is ABC N in D in B? It is here, it is a marker. So the B is a marker based whereas A, it is just identifying the wrist and putting the overlay of the digital watch that how this watch is suiting or not. So this is a marker less OK. This one is projecting a dinosaur and uh uh on the top top of this particular diagram. And uh this one is basically your super imposition of the um your digital at the top of the real world. So this is what um is some guess on some more examples I gave, I'll go to the chat box and just check and kind. Is it clear? Now I gave her a quick recap. Can I proceed? Oh, thank you. Thank you. Thank you. So I'll again share. I don't know whether it is. OK. OK. So this is what one example we have done. So now coming to the computer vision, the topic is computer vision for Ar and VR.
So computer vision is actually a part of a field of artificial intelligence and it allows us to see, observe, understand and make an informed decision. So if you see this figure, the task is there are some fruits on the plate. And I want to list down all the fruits. If as a human being, I see the fruits, I identify and recognize the fruits, my brain processes them by recognizing them. And finally I list it out. Now, if I want to automate this, if I want to automate this, then I need a sensing device. First of all, to capture what is in the plate. So that is called the image, the sensing device. Now I want to have an interpreting device or the algorithm to recognize each of these fruits. After that, I'll provide the list of the fruits. So the whole a concept of the computer vision is see, observe, understand and then act. So these are some of the computer vision tasks. We'll go one by one, we will go one by one. OK. Let us start with here here. I'm trying to detect the vehicles, whatever vehicles are there, I'm just detecting. So I'm putting a bounding box, if it is an object recognition, I will say this is a car or this is a truck. Oh This is uh uh a bus something.
What is object tracking tracking is if I pinpoint this particular car and I will track where it is going, whether it has met with an accident, what is the speed limit? So it is a tracking is usually with the videos coming to this image of one image will be classified as one label, a label will be given. So it is identifying that this is a cat. It can be a multi class classification as well. If you have a cat and a dog in one image, then it will show it will tell you there are two classes. OK? Next one is classification and localization localization means putting a bounding box for the object. So it is localizing it. Next is semantic segmentation, semantic segmentation.
If in the left hand side, if you see here, then this is the cat, this is the grass, the trees are shown here and the sky is this blue color. So semantic meaningful segmentation has been done. So it is not only objects the pixels are getting clustered in one meaningful manner. Here, we are not saying that this particular thing is a cat or a tree or a sky, but all of them are given a different color. If we want instant segmentation, then apart from segmenting, there are three cat classes, multi classes I told you cat dog duck. So the cats are in red color boundaries. Duck is in green color and the dog is in blue color. Next is feature extraction. So these are all computer vision tasks which are used for the A RVR in the feature extractor. It is designed to take all the gradients wherever the edges are there or where there is a curvature. Now there is an optical character recognition where depending on the anyone's handwriting, I am able to identify which character or alphabet the person has written any questions kind uh Kindly put it in the chat box. Otherwise I will proceed. Shall I proceed, Cathy not, can I proceed, please?
Any doubts you have? OK. Next, another computer vision task with natural language processing. So here we are not only giving one word but we are generating a sequence of words which is a meaningful sentence. So if you see the classification at the left hand side, it is for the whole image, it is for the whole image girl for the whole image. This is another task called captioning. A girl is playing tennis and the girl is playing with black box. So now coming to this hand recognition and marker list. So now when we develop the software for artificial or augmented reality and uh your uh virtual reality, then it has to do all these things, classify, detect, recognize track segment feature detection. All of these have to be done at the preliminary stage. So now if I we see this as an example of marker less augmented reality, where you want to see whether the ring suits you or not at the ring finger, then it identifies the ring finger and the overlays this digital ring at the top of it. The second in the second uh example is marker based. So this is the marker, this is the market we are having here. And after that, the product has to be displayed in the pamphlet of the.
So this is the market based where the product uh is in the pamphlet is shown as a 3D. It is rendered as a 3d. Another very important computer vision task is simultaneous localization and mapping also called slam. So the VR will be giving you a virtual map of the environment for marker based augmented reality. A tracking can be done for a fixed user location. For marker less A R you can track a user wherever he is going. So in marker based, you will look for only the markers where the user is going because it's a fixed for marker less irrespective of any marker. It is, it will be continuously tracking the user. While you con continuously tracking the user, you can make a virtual map of the environment. So this is one case study of health, health and fitness. There's a treadmill, the conventional treadmill, which is mechanical. Nowadays, companies are coming up with IO and augmented reality treadmill where you can train yourself for mountaineering, you can train yourself for mountaineering and trekking at your home itself. If you see here, the picture, this is the guide, there is a software which where you will have a guide and the guide will take you to the mountains and the uh your the slope, the alignment will be simulated similarly in the treadmill.
So if it is a steep in a steep climb, the same IOT based uh treadmill will make it steep. And in the screen, you can see that you are walking in the mountains and that's why it is steep. When you come down, when you climb down, then the IOT again makes in the treadmill a slope type so that you do not feel any problem while climbing down. But this is not an immersive experience because this immersive experience can happen only if you see the last one where this is the virtual world in which you feel as if you are going inside it. So it is fully immersive and you will have so many gadgets at the hand, the sound, the goggles, so many like as if there will be many senses iot sensors to make you feel, feel fully immersive. So this type of treadmill is in research. It's not yet there uh for the common man and presently many of them are using this IOT and the augmented reality based treadmills. This is a R application in tourism industry. So this is, can you tell this is marker based or mark less based or it is marker or markers? OK. So here this is GPS location based.
So in the GPS location based, depending on this GPS location, it knows through the GPS that this is a restaurant, this is coffee shop. So this is augmented reality. Why? Because this information is being overlaid in the real world. This is an air application for an architect and client. So here it is super imposing from the pla plan two D plan. The 3D is getting uh rendered in in the screen. This is virtual reality for interactive learning. So both uh the humans are having both the persons are having goggles and they are interacting with each other with a virtual world where this plane is there. Again, this is the virtual rendering where they both are able to interact. The software development environment are various like unity and euphoria are very much commonly when popularly used Arki is from Apple Ar core, from Google Wiki and OPENCV is all about the computer vision. So let's be ready for the future because the Gartner 2023 strategic technology trends have been released where they have already mentioned metaverse as the ninth in the ninth, the topic is already there. The metaverse technology. So can A IVR exist without CV? No, because the CV is the fundamental of it. So these are all the references I would like to thank and acknowledge Vasary College of Engineering Hyderabad, India and Women Tech Network for giving me this opportunity. Thank you, Namaste. Any questions please feel free to ask. Thank you.
First name, I'm able to see. OK, this is at a very nascent stage. So I have collected uh I have researched through various blogs and uh the software manuals and this, I couldn't find uh really a one shot place where I can get each and everything and it's evolving. So I and I have put all the references anyway. So those references are mostly blogs or some research papers. Thanks a lot. Any other questions?